Did you know 34% of Americans have errors on their credit reports? Fixing these mistakes could boost your score fast! This guide reveals legal credit repair tips to help you rebuild financial health.
【Credit Score Fundamentals Decoded】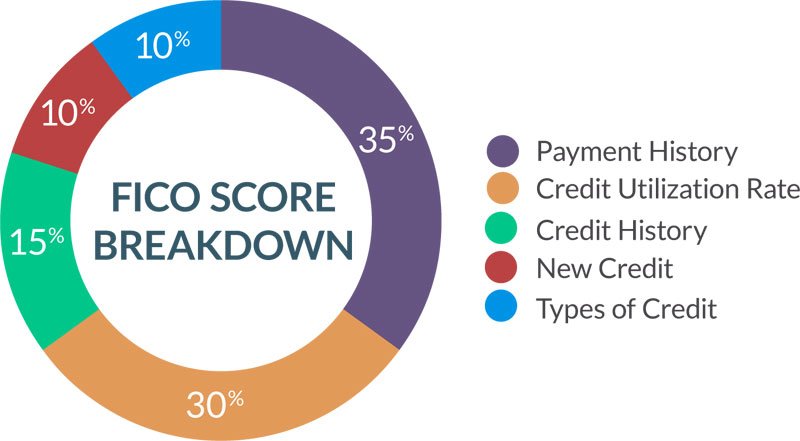
What Your Credit Score Really Measures
Your credit score isn’t a judgment on your character; it’s a statistical prediction. Lenders use this three-digit number, primarily generated by Equifax or TransUnion in Canada, to answer one core question: “How likely is this person to repay borrowed money on time?” Think of it as a risk snapshot based purely on your past financial behaviour documented in your credit report. It distills complex data into a single, comparable figure that determines the credit offers you receive and the interest rates you pay in 2025. It doesn’t factor in income, savings, job history, or demographic details like race or gender – solely your credit management patterns.
The 5 Key Credit Score Factors
Your score is built from five pillars, each with distinct weight:
- Payment History (35% Impact): The single most crucial element. It tracks whether you’ve paid credit accounts (credit cards, loans, mortgages) on time. Late payments, collections, bankruptcies, or defaults here cause significant damage. Consistent on-time payments are paramount.
- Credit Utilization Ratio (30% Influence): This measures how much of your available revolving credit (mainly credit cards and lines of credit) you’re using. Calculated per card and overall. Example: A $2,000 balance on a card with a $10,000 limit = 20% utilization. Crucially, experts recommend keeping this ratio below 30% overall and per card for optimal scoring. High utilization signals potential overextension. For more on managing credit utilization, check out 5 Brutal Truths About Balance Transfer Credit Cards for Bad Credit.
- Credit History Length (15%): This considers the age of your oldest account, the age of your newest account, and the average age of all your accounts. A longer, well-managed credit history generally benefits your score, demonstrating experience.
- Credit Mix (10%): Lenders like to see you can handle different types of credit responsibly. This includes revolving credit (credit cards, lines of credit) and installment loans (car loans, mortgages, student loans). Having a mix is slightly beneficial, but it’s not wise to open accounts just for this.
- New Credit Inquiries (10%): When you apply for new credit, a “hard inquiry” is recorded on your report. Several hard inquiries within a short period (especially for credit cards) can lower your score, as it may suggest financial stress or credit-seeking behaviour. Checking your own credit report is a “soft inquiry” and does not affect your score. Learn how to Remove Hard Inquiries from Your Credit Report.
Canadian Credit Score Ranges Explained
Canadian credit scores typically range from 300 (very poor) to 900 (exceptional), though models can vary slightly. Understanding where you fall is key to knowing your borrowing power:
| Score Range | Rating | What It Means in 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| 300 – 559 | Poor | Significant credit challenges exist. Loan/credit approval is difficult and expensive (very high interest). Securing housing/utilities may require extra deposits. Urgent repair needed. |
| 560 – 659 | Fair | Below average, indicating some past issues or limited history. Approval possible but often at higher-than-average rates. Room for significant improvement. |
| 660 – 724 | Good | Meets the threshold for most mainstream lenders. Qualifies for decent rates, though not the absolute best. A solid foundation to build upon. |
| 725 – 759 | Very Good | Significantly better than average. Qualifies for favourable interest rates and better terms on loans and credit cards. |
| 760 – 900 | Excellent | Prime borrowing territory. Demonstrates exceptional credit management. Qualifies for the lowest possible interest rates and the best credit card rewards/offers. Negotiating power is highest here. |
Excellent vs. Poor Scores Defined
- 760+ (Excellent): This is the golden zone. Borrowers here enjoy the absolute best terms available in 2025 – think mortgage rates significantly below average, premium credit cards with lucrative rewards and low fees, and high approval odds. It represents the lowest perceived risk to lenders.
- Below 560 (Poor): Scores in this range signal substantial risk to lenders based on past behaviour (like chronic late payments, collections, or defaults). Getting approved for traditional loans or unsecured credit cards is extremely challenging. If approved, interest rates will be punitive. Rebuilding requires focused effort, often starting with addressing negative items and establishing positive payment patterns. Understanding these fundamentals is the first step toward taking control. For a personalized strategy to move into that prime 760+ territory or repair a score below 560, explore the tailored solutions at
fixcreditscenter.com.
【Top Fix Your Credit FAQs Answered】
Why Payment History is King
Your payment history isn’t just a factor; at 35% of your score, it’s the cornerstone. Lenders in 2025 scrutinize this above all else because it directly answers their core question: “Will this person pay us back on time?” Past behaviour remains the strongest predictor.
Establishing Rock-Solid Payment Patterns
Building an impeccable history requires proactive systems, not just good intentions:
- Set Payment Reminders 3 Days Before Due Dates: Don’t rely on memory or the grace period. Life happens. An alert 72 hours prior gives you buffer for bank processing times or unexpected delays. Automate payments for absolute certainty if your cash flow allows.
- Understand Minimum Payment Consequences: Making only the minimum keeps your account “current” and avoids immediate default fees from the lender. Crucially, however, if your payment is even one day late beyond the due date and less than 30 days late, the lender may charge a fee, but it generally won’t be reported to the credit bureaus as “late” yet. The critical threshold is 30+ days late. Payments arriving 30, 60, 90, or 120+ days past due will be reported to Equifax and TransUnion, causing severe score damage. Consistently paying the minimum on time is vastly better than missing a payment, but paying the full balance avoids interest and faster debt reduction. For strategies on fixing late payments, see 7 Power Moves to Fix Credit Score After Late Payments.
Recovering From Past Mistakes
Old late payments or defaults aren’t a life sentence. The system is designed to reward improvement:
- Good History Eventually Outweighs Old Lates: While negative items (like late payments, collections) stay on your report for 6-7 years in Canada, their impact lessens over time, especially as positive information accumulates. Consistent, perfect payment behaviour after a mistake demonstrates you’ve changed your habits. A single 30-day late from 4 years ago hurts far less than one from last month.
- Consistent On-Time Payments Rebuild Trust: There’s no magic shortcut. Every single on-time payment you make after a mistake is a brick in rebuilding your credibility. Lenders see a pattern of reliability emerging, gradually offsetting past risk. This takes patience and unwavering discipline – but it works. To fix credit issues related to collections, consider 7 Proven Ways to Fix Credit with Collections Fast.
Mastering Your Credit Utilization Rate
Your credit utilization ratio – how much revolving credit you’re using compared to your limits – is the second most powerful factor (30%). It’s a real-time indicator of potential financial strain.
Calculating Your True Utilization
Understanding your number is step one:
- Formula: (Total Balances ÷ Total Limits) x 100 = Utilization %. Calculate this both per individual card and across all your revolving accounts (credit cards, lines of credit). Example: If you have two cards ($1,000 balance on Card A with $5,000 limit, $500 balance on Card B with $5,000 limit), your total utilization is ($1,000 + $500) / ($5,000 + $5,000) = $1,500 / $10,000 = 15%.
- Ideal Target: Below 30% Consistently. While lower is better (under 10% is often cited for maximizing scores), staying below 30% overall and per card is the widely recognized benchmark for avoiding negative impacts in 2025. Exceeding this signals potential reliance on credit and higher risk.
Practical Reduction Strategies
Lowering your utilization doesn’t necessarily require paying off massive debts overnight:
- Request Credit Limit Increases Strategically: If you have a card in good standing (no recent lates, low utilization on that card), a successful limit increase instantly lowers your utilization ratio without requiring extra payment. For example, a $1,000 balance on a card with a $5,000 limit is 20% utilization. If the limit increases to $7,000, the utilization drops to ~14% with no change to your balance. Caution: Only request increases sparingly, as the issuer will likely perform a hard inquiry. Don’t request if you anticipate needing a major loan (mortgage, car) soon.
- Make Multiple Payments Monthly: Don’t wait for the monthly statement. If you use a card frequently, pay down the balance before the statement closing date. The balance reported to credit bureaus is typically your statement balance. Lowering it before it’s reported keeps your utilization low. Example: If you charge $1,500 during a billing cycle on a card with a $5,000 limit, paying $1,000 before the statement generates means only a $500 balance is reported (10% utilization), not $1,500 (30%).
Mastering these two pillars – payment history and utilization – forms the bedrock of credit repair and achieving a prime score. For a personalized plan tackling your specific challenges and leveraging the latest 2025 strategies, discover how fixcreditscenter.com can guide your journey to 760+.
【Tackling Credit Report Errors】

Your credit report is the foundation lenders scrutinize in 2025. Even minor inaccuracies can unfairly depress your score. Spotting and disputing errors is non-negotiable for true credit health.
Spotting Common Inaccuracies
Errors are surprisingly frequent. Vigilance is your first line of defense:
- Incorrect Account Status: Verify every account is correctly marked as “Open,” “Closed,” or “Paid.” An account erroneously shown as “Open” with a balance when you closed it years ago inflates your perceived debt and utilization ratio. Similarly, an account mistakenly marked “Closed” by the lender but still reported as “Open” can cause confusion and potential scoring issues.
- Duplicate Collection Entries: A single debt sold between collectors often appears multiple times. This falsely amplifies your debt burden and number of derogatory marks. Scrutinize collection accounts for identical amounts, dates, and creditor names – duplicates must be challenged.
Frequent Error Types
Beyond the major categories, watch for these pervasive issues:
- Outdated personal information (old addresses, misspelled names)
- Accounts belonging to someone with a similar name (a common mix-up)
- Inaccurate payment history (showing late payments you made on time)
- Incorrect credit limits or loan amounts
- Accounts fraudulently opened due to identity theft
The Step-by-Step Dispute Process
Finding an error is step one; getting it fixed requires a precise, documented approach. In 2025, persistence and proper procedure are key.
Contacting Credit Bureaus (Equifax & TransUnion)
This initiates the formal investigation:
- Obtain Your Reports: You must dispute directly with the bureau reporting the error. Get your official reports from Equifax.ca and TransUnion.ca.
- Draft Your Dispute Letter: Clearly identify each error and state why it’s incorrect. Be specific (e.g., “Account #XXXXX is reported as Open with a $500 balance. I closed this account in 2023 and have confirmation letter dated MM/DD/2023.”).
- Gather & Attach Proof: Include copies (never originals) of required documentation: bank statements, payment confirmations, closure letters, ID, and a copy of the report with the error highlighted. Proof is mandatory – claims without evidence are often dismissed.
- Send via Certified Mail: This provides tracking and proof of receipt. Keep copies of everything you send. Bureaus typically have 30 days to investigate from receipt.
Notifying Data Furnishers (The Original Creditor/Collector)
Simultaneously alert the source of the data:
- Identify the Furnisher: This is the bank, lender, credit card issuer, or collection agency reporting the incorrect information.
- Send a Separate Dispute: Draft a similar letter with the same specifics and proof as sent to the bureaus. Address it to their disputes department (often found on your statement or their website).
- Document Everything: Send via certified mail with tracking. Under Canadian law, the furnisher investigation timeline is 30 days maximum upon receipt. They must investigate and report findings back to the bureaus.
Errors won’t fix themselves. A meticulous, evidence-backed dispute process is your right and your most powerful tool for an accurate report. For expert guidance navigating disputes in 2025 and leveraging advanced tactics, explore tailored solutions at fixcreditscenter.com.
【Rebuilding Bad Credit Realistically】

A low credit score in 2025 feels like quicksand, but escape is methodical, not miraculous. True credit repair demands disciplined financial behavior over time. Forget shortcuts; focus on proven tools that rebuild trust with lenders by demonstrating consistent responsibility.
Secured Credit Card Strategy
Think of a secured card as training wheels for credit. You provide a refundable security deposit upfront, which becomes your credit limit. This collateral drastically reduces the lender’s risk, making approval highly accessible even with significant credit dings. In 2025, secured cards aren’t a niche product but a mainstream rebuilding tool, with approval rates exceeding 89% for applicants with sub-600 scores.
How Secured Cards Build History
The mechanics are simple yet powerful:
- Collateral Requirement: You fund the security deposit, typically between $100 and $500. This amount directly sets your spending limit. Choose a deposit you can afford but that provides enough room for manageable, recurring usage.
- Activity Reporting: Crucially, your card activity – purchases and, most importantly, on-time payments – is reported monthly to both major credit bureaus (Equifax and TransUnion). This injects fresh, positive data into your report, gradually diluting past negatives.
- Graduation to Unsecured: After consistently demonstrating responsible use (usually 12-24 months of on-time payments and keeping utilization low), many issuers will automatically “graduate” your account. You receive your deposit back, and the card converts to a traditional, unsecured credit card, reflecting significant trust regained. This graduation is a tangible milestone in your credit recovery.
Debt Repayment Strategies That Work
Outstanding debt is an anchor on your score. Choosing a structured repayment method isn’t just about clearing balances; it’s a psychological and financial blueprint for recovery. Two dominant strategies have proven effective in 2025:
Snowball vs. Avalanche Method
The core difference lies in which debt you prioritize:
| Method | How it Works | Key Psychological Driver | Primary Financial Benefit | Best For… |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snowball | List debts smallest balance to largest. Pay minimums on all, then throw every extra dollar at the smallest debt first. Once paid off, roll that payment amount to the next smallest. | Quick Wins: Eliminating a debt entirely provides immediate motivation and a sense of accomplishment early on. | Faster elimination of individual accounts, reducing total number of debts quickly. | Individuals needing early momentum boosts to stay committed. |
| Avalanche | List debts highest interest rate to lowest. Pay minimums on all, then direct all extra funds to the debt with the highest interest rate. Once paid off, move to the next highest rate. | Maximum Savings: Knowing you’re minimizing the total interest paid provides strong long-term rationale. | Saves the most money on interest over the repayment journey. | Individuals focused purely on the math and long-term cost savings. |
Both methods require strict budgeting. The critical factor isn’t which one is “best” overall, but which one you can sustain consistently. Sticking to either plan rigorously is infinitely more valuable than sporadically attacking debts without a system.
Rebuilding credit is a marathon paced by smart tactics. Leveraging secured cards strategically and attacking debt systematically creates the undeniable positive history lenders demand. For a personalized 2025 roadmap incorporating these fundamentals with advanced optimization, expert guidance is available at 7 Proven Ways to Fix Your Credit and Buy a House.
【Debunking Credit Repair Myths】
The desperation to escape bad credit breeds a fertile ground for misinformation. In 2025, promises of instant score jumps or “guaranteed deletions” flood the digital landscape, preying on hope while delivering little but frustration and wasted fees. Understanding why these myths persist – and why they fail – is crucial for navigating a genuine path to recovery.
The Truth About “Quick Fixes”
The allure of a rapid credit score transformation is powerful, yet fundamentally at odds with how credit reporting works. Legitimate credit repair is a process, not an event.
Why Most Credit Repair Promises Fail
- Accurate Negative Info Can’t Be Magically Removed: Federal law (the Fair Credit Reporting Act) mandates that credit bureaus can only remove information proven to be inaccurate, outdated, or unverifiable. If a late payment or collection account is correctly reported and belongs to you, no legitimate service can wave a wand to erase it. Promises to remove accurate, timely negative items are red flags for scams.
- Legitimate Disputes Require Documentation: Successfully challenging an error demands evidence. Reputable services meticulously review your reports line-by-line, identifying genuine inaccuracies (e.g., accounts you didn’t open, payments marked late when paid on time, duplicate collections). They then file disputes supported by documentation with the bureaus and creditors. This takes time and effort; it’s not a bulk dispute or frivolous challenge designed solely to temporarily obscure negative data. Services promising mass disputes without concrete proof of errors offer little lasting value.
DIY vs. Professional Credit Counselling
While managing credit repair yourself is possible with diligence, professional guidance offers structure and negotiation leverage in specific, complex situations.
When Credit Counselling Makes Sense
- Debt Management Program (DMP) Benefits: Non-profit credit counseling agencies specialize in DMPs. They negotiate directly with your creditors to secure concessions like lower interest rates, waived late fees, and a single consolidated monthly payment. Enrolling in a DMP typically requires closing the included credit card accounts, but consistent on-time payments under the plan are reported positively to bureaus. This structured approach is powerful if you’re overwhelmed by multiple high-interest debts but have a stable income to make the consolidated payment.
- Non-profit vs. For-profit Service Differences: Distinguishing these models is critical:
Feature Reputable Non-Profit Credit Counseling Agency For-Profit Credit Repair Service Primary Focus Debt management, budgeting education Disputing credit report items Fees Low setup/mo. fees (often regulated), sometimes free initial consult Often high upfront/monthly fees DMP Access Yes, through creditor agreements No “Guarantees” No unrealistic score jump promises Often make lofty, unattainable guarantees Transparency Clear fee structure, non-profit status Can be opaque, aggressive sales tactics Non-profit counseling focuses on sustainable behavior change and debt repayment, while for-profit repair often focuses solely on disputing report entries – a tactic with limited effectiveness against accurate information. For a structured 2025 strategy navigating these complexities, explore the tailored solutions at fixcreditscenter.com.Urgent Fix Your Credit Questions
The shadow of past financial missteps looms large, particularly when you’re actively trying to rebuild. Understanding the lifespan of negative marks and the realistic path forward after major setbacks like bankruptcy is critical for managing expectations and formulating an effective 2025 strategy. Here’s what you need to know about timelines.
How Long Negative Info Stays
Credit reporting operates on defined timeframes governed by consumer protection laws. While the impact lessens over time, negative items have a fixed shelf life on your reports.
Standard Reporting Timeframes
- Late Payments: A single late payment can significantly dent your score, but its reporting lifespan is finite. In Canada, late payments generally remain on your credit report for 6 years from the date you first became delinquent on that account and never subsequently brought it back to a current status.
- Bankruptcy: The reporting period depends on the type of bankruptcy filed and provincial regulations:
Bankruptcy Type Standard Reporting Period Key Consideration First-Time Bankruptcy (Summary/Ordinary) 6 years from discharge (or 7 years in some provinces) Discharge typically takes 9-21 months Second Bankruptcy 14 years from discharge Significantly longer impact Proposal (Consumer Proposal) 3 years after you fulfill the proposal terms Remains for 3 years after completion These are maximum reporting periods. Credit bureaus must remove the items once this timeframe expires. Proactive removal before the legal date is only possible if the information is proven inaccurate. Improving Scores After Major Setbacks
A major negative event like bankruptcy feels catastrophic, but recovery is a structured process, not a mystery. Patience and consistent positive behaviour are paramount.
Post-Bankruptcy Recovery Timeline
- Immediate Focus (Month 1): Obtain your official discharge documents. Order your credit reports to confirm the bankruptcy is accurately reported (showing “Discharged” status and the expected removal date). Secured credit card approval is often possible immediately post-discharge. This involves providing a cash deposit (e.g., $500) which becomes your credit limit. Use it minimally (under 30% of the limit) and pay it off in full every month without fail.
- The Rebuilding Phase (Months 1-24): Diligently manage the secured card. After 6-12 months of perfect payment history, explore adding another small credit product, potentially a credit-builder loan or a retail card with a low limit. Continue flawless payments and keep utilization very low. Avoid applying for too much credit too quickly.
- Significant Improvement (Years 2-3): With 2-3 years of consistent, impeccable credit behaviour post-discharge – including on-time payments on all accounts and low credit utilization – your score can see substantial recovery. The negative impact of the bankruptcy itself diminishes as it ages. You may qualify for standard unsecured credit cards and better loan terms. The bankruptcy record remains visible but lenders increasingly weigh your recent positive track record.
- Long-Term Stability (Year 6/7+): Once the bankruptcy falls off your report (after 6 or 7 years, depending on type and province), your score can fully reflect your rebuilt positive history, assuming continued responsible management. Achieving scores well into the “good” or even “excellent” range is entirely possible.
The path demands discipline, but the structure is clear. For navigating the specific nuances of rebuilding in 2025, especially post-bankruptcy, the evidence-based approaches at
fixcreditscenter.comoffer a proven framework tailored to Canadian credit systems.Previous Blog Posts:
5 Brutal Truths About Balance Transfer Credit Cards for Bad Credit, How to Remove Hard Inquiries from Your Credit Report, 7 Power Moves to Fix Credit Score After Late Payments, 7 Proven Ways to Fix Credit with Collections Fast, 7 Proven Ways to Fix Your Credit and Buy a HouseKey Takeaways for Effective Credit Repair
By now, you’ve learned how to check reports for errors, dispute inaccuracies, and build positive credit habits. Remember: consistent payments and smart credit use are your best tools.
Ready to take action? Visit https://fixcreditscenter.com now for personalized help. Share your success story in the comments below!

